- Neurodegenerative diseases (NDD) are among the most common causes of disability and mortality worldwide; progressively imposing a tremendous socio-economic burden and a massive medical emergency with no current solution in sight. Available treatment have minimal or no effect on the progression of NDD.
- Neuropathology in most NDDs such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson disease (PD), Lewy body dementia (LBD) and prion disease are characterised by the conformational change of an otherwise soluble physiological protein/peptide into a pathological conformer with dominant β-sheet secondary structure. This results in oligomers and fibrils causing loss of function and gain of toxicity.
- The change in conformation towards the misfolded conformers opens the window for immunological intervention. Therefore, immunotherapy either active or passive, has been deemed to be a valid therapeutic option for NDD.
- Alzheimers, the most common NDD, neuropathology consist of the accumulation of amyloid β (Aβ) as amyloid plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), as well as the misfolded hyperphosphorylated tau as neurofibrillary tangles (NFT). However, the most toxic species of Aβ and aggregated tau are thought to be mis-folded oligomeric with dominant β-sheet secondary structure, which might help to spread the pathology in a prion-like mechanism. On the other hand the pathogenesis of PD, LBD and prion disease are associated with aggregation/oligomerisation of α-synuclein and PrP, respectively.
- The complexity of having more than one oligomeric self-conformer involved in the pathology of any NDD possesses the problem of how to induce an immune response to address the both concurrent pathologies of Aβ and tau in AD and the different strains of prion diseases. The induced immune response should be able to only target the toxic oligomers, sparing the normal self-protein/peptides and avoiding autoimmune toxic inflammation.
- Most of all previous attempts to use active or passive immunization directed to either Aβ or tau conformers in AD have failed during clinical trials. This is mainly due to addressing one side of the pathology or the unwanted autoimmune toxicity with clear vascular and amyloid related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) manifestations produced after the antigen-antibody (Ab) recognition.
- Recently, some conformational immunogens based on the primary structure of Aβ have been developed. However, their use did not produce any significant advancement over the previous methods.
- To overcome all these hurdles we have developed a methodology to induce only a specific Ab response to the β-sheet secondary structure present in pathologic oligomers, by the use of a generic, non-self β-sheet rich oligomeric immunogen (Goni et al., Scientific reports 2017), as shown in Figure 1.
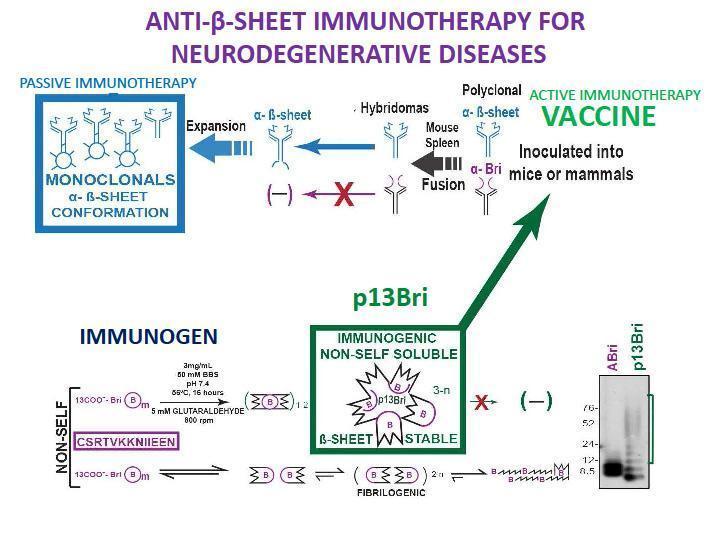
- The active vaccination with the p13Bri immunogen produced a significant cognitive rescue, lower pathology and no vascular side effects in many different AD transgenic (Tg) animal models, including those prone to vascular pathology. The production of monoclonal Ab with the same type of immunization produced families of anti-β-sheet conformational monoclonal Abs (aβComAb) that recognize all kind of pathologic oligomers present in AD and other NDDs. Some of the aβComAb, including IgM, showed a good penetration of the blood-brain-barrier and produced significant cognitive rescue and lower pathological oligomers of both Aβ and tau in old animals of an AD Tg model with flourished Aβ and tau pathologies. No side effects were recorded to this immunotherapy.
- The transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are a large group of related neurodegenerative conditions, which affect animals and humans. Included among others are kuru and variant Creutzfeld Jacob disease (vCJD) in humans, bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE, or “mad cow disease”) in cattle, chronic wasting disease (CWD) in deer, moose and elk, and scrapie in sheep. These diseases all have long incubation periods, up to 56 years recorded for kuru in humans; but rapidly progress once clinical symptoms begin. All prion diseases are fatal with no effective form of treatment, currently.
- CWD is the most infective and devastating form of prion disease causing epidemics among cervids in North America (USA and Canada), and some reported free range cases in Europe, particularly in Norway, and Korea. CWD has been shown to be transmitted to felines and primates (squirrel monkeys). Although no cases of transmission to humans have been documented, the increasing number of animals infected in herds and in the wild pose a real threat of eventual species jump to infections in humans.
- To specifically address the problem of the transmissible prion diseases; an active mucosal vaccination was developed to protect the gastrointestinal tract – the main point of entry of the infective prions. Species specific PrP and PrP fragments sequences were incorporated into an attenuated Salmonella that acted as a delivery system to lymphoid cells in the gut overcoming self-tolerance and producing a sustainable anti-PrP sIgA in saliva and faeces that showed protection in mouse models for adapted scrapie and in white tail deer from CWD (Goni et al. 2014).